Automatic Scaling
Scaling is the ability to adjust available resources to meet client demands. Services can be scaled manually by calling an API programmatically, or changing settings on the UI to adjust system resources. Alternatively, services can be autoscaled to meet application demands.
Scaling is only applicable to Production tier services. Development tier services do not scale. You can upgrade a service from Development tier to Production in order to scale it. Once a Development service is upgraded, it cannot be downgraded.
How scaling works in ClickHouse Cloud
ClickHouse Cloud scales services based on CPU and memory usage. We constantly monitor the historical usage of a service over a lookback window. If the usage rises above or falls below certain thresholds, we scale the service appropriately to match the demand. The larger of the CPU or memory recommendation is picked, and CPU and memory allocated to the service are scaled in lockstep increments of 1 CPU and 4 GiB memory.
Vertical and Horizontal Scaling
By default, ClickHouse Cloud Production services operate with 3 replicas across 3 different availability zones. Production services can be scaled both vertically (by switching to larger replicas), or horizontally (by adding replicas of the same size). Vertical scaling typically helps with queries that need a large amount of memory for long running inserts / reads, and horizontal scaling can help with parallelization to support concurrent queries.
In the current implementation, vertical autoscaling works well with slow incremental growth in memory and CPU needs. We are working on improving it to better handle workload bursts.
Autoscaling currently only scales a service vertically. To scale a service horizontally (currently in private preview), you would need to do this via the Cloud API. To enable horizontal scaling on your service please contact support@clickhouse.com and see the section Self-serve horizontal scaling.
Configuring vertical auto scaling
The scaling of ClickHouse Cloud Production services can be adjusted by organization members with the Admin role. To configure vertical autoscaling, go to the Settings tab on your service details page and adjust the minimum and maximum memory, alongwith CPU settings as shown below.
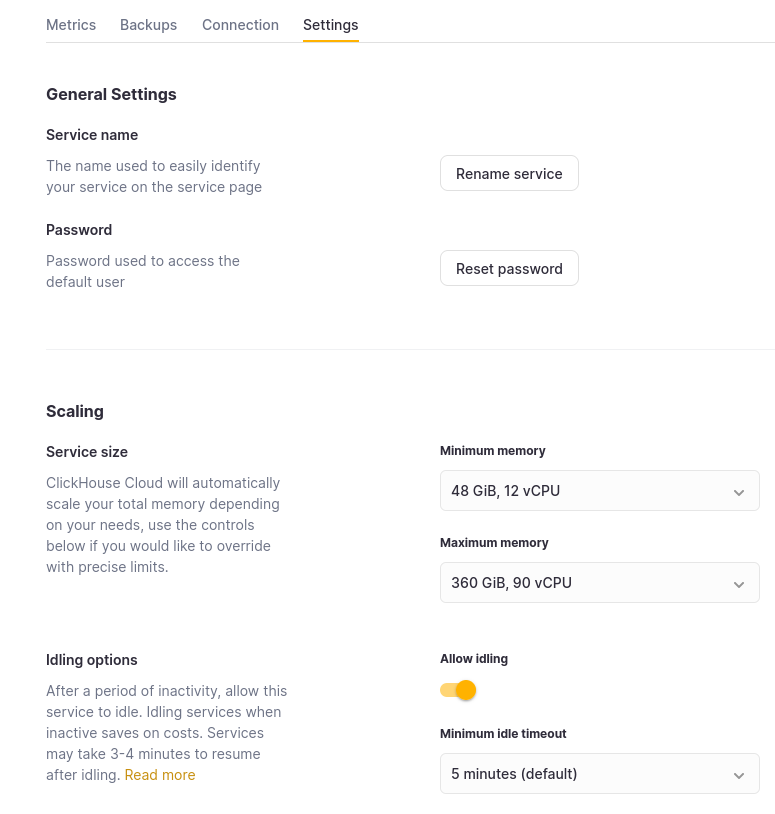
Set the Maximum memory for your replicas at a higher value than the Minimum memory. The service will then scale as needed within those bounds. These settings are also available during the initial service creation flow. Each replica in your service will be allocated the same memory and CPU resources.
You can also choose to set these values the same, essentially pinning the service to a specific configuration. Doing so will immediately force scaling to happen to the desired size you picked. It's important to note that this will disable any auto scaling on the cluster, and your service will not be protected against increases in CPU or memory usage beyond these settings.
Self-serve horizontal scaling
ClickHouse Cloud horizontal scaling is in Private Preview. Once horizontal scaling is enabled on the service, you can use ClickHouse Cloud public APIs to scale your service by updating the scaling settings for the service.
- If the feature has not been enabled on the service, the request will be rejected with the error
BAD_REQUEST: Adjusting number of replicas is not enabled for your instance".Please reach out to ClickHouse Cloud support if you see this error and you think scaling has already been enabled on your service. - A Production ClickHouse service must have a minimum of
3replicas. Currently, the maximum number of replicas a Production service can scale out to is20. These limits will be increased over time. If you need higher limits for now, please reach out to the ClickHouse Cloud support team. - Currently the system table data for replicas that are being removed during a scale-in operation is not being preserved. This could affect any dashboards or other functionality that might be leveraging the system table data.
Horizontal scaling via API
To horizontally scale a cluster, issue a PATCH request via the API to adjust the number of replicas. The screenshots below show an API call to scale out a 3 replica cluster to 6 replicas, and the corresponding response.
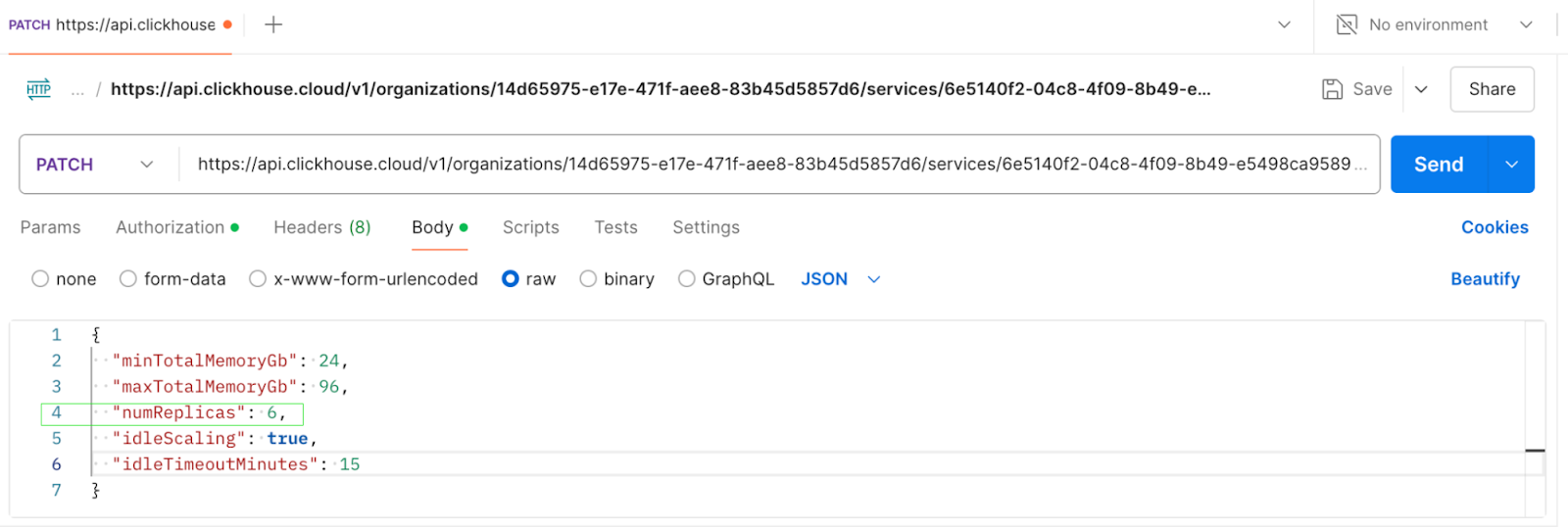
PATCH request to update numReplicas
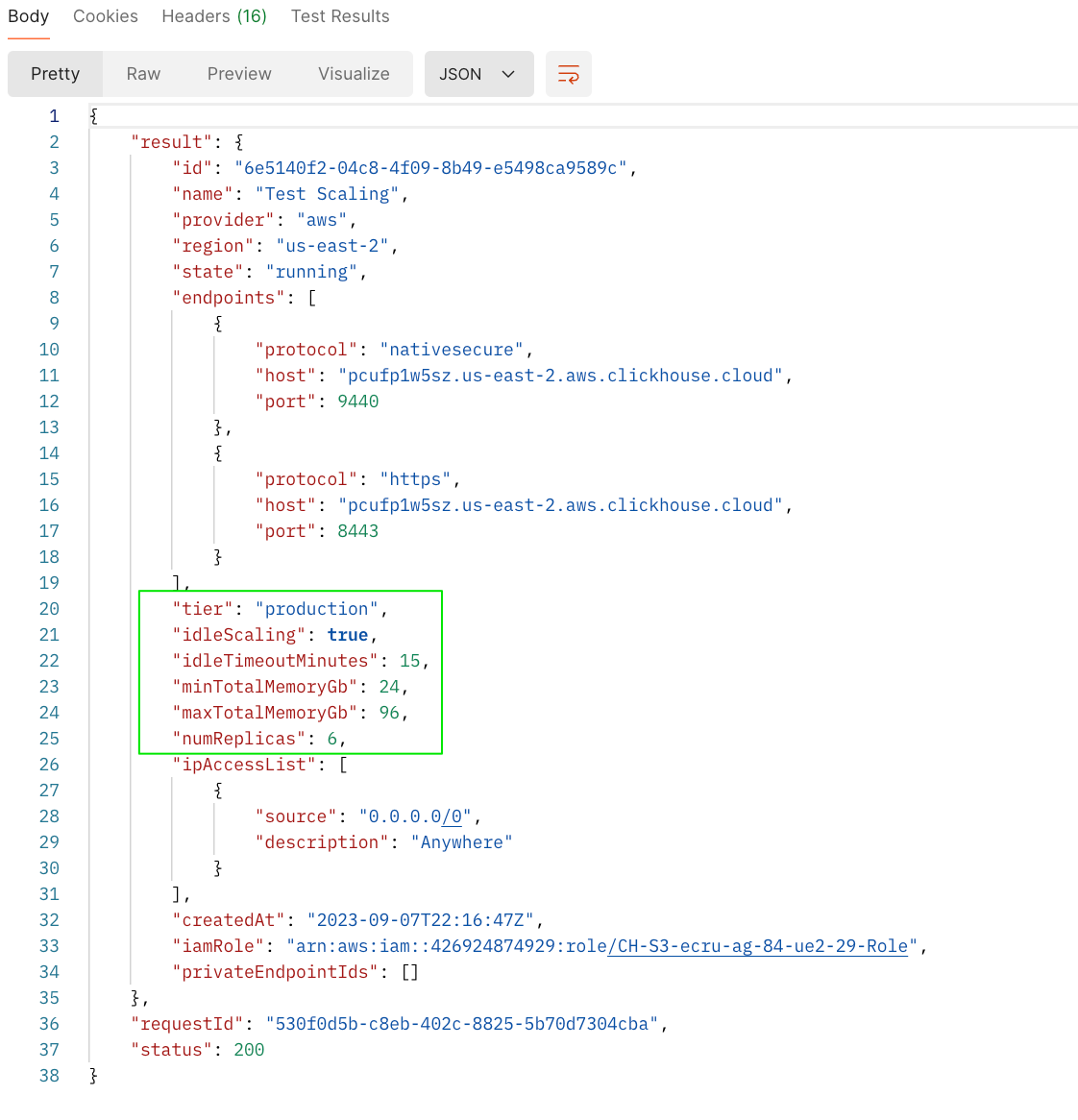
Response from PATCH request
If you issue a new scaling request or multiple requests in succession, while one is already in progress, the scaling service will ignore the intermediate states and converge on the final replica count.
Horizontal scaling via UI
To scale a service horizontally from the UI, you can adjust the number of nodes for the service on the Settings page.
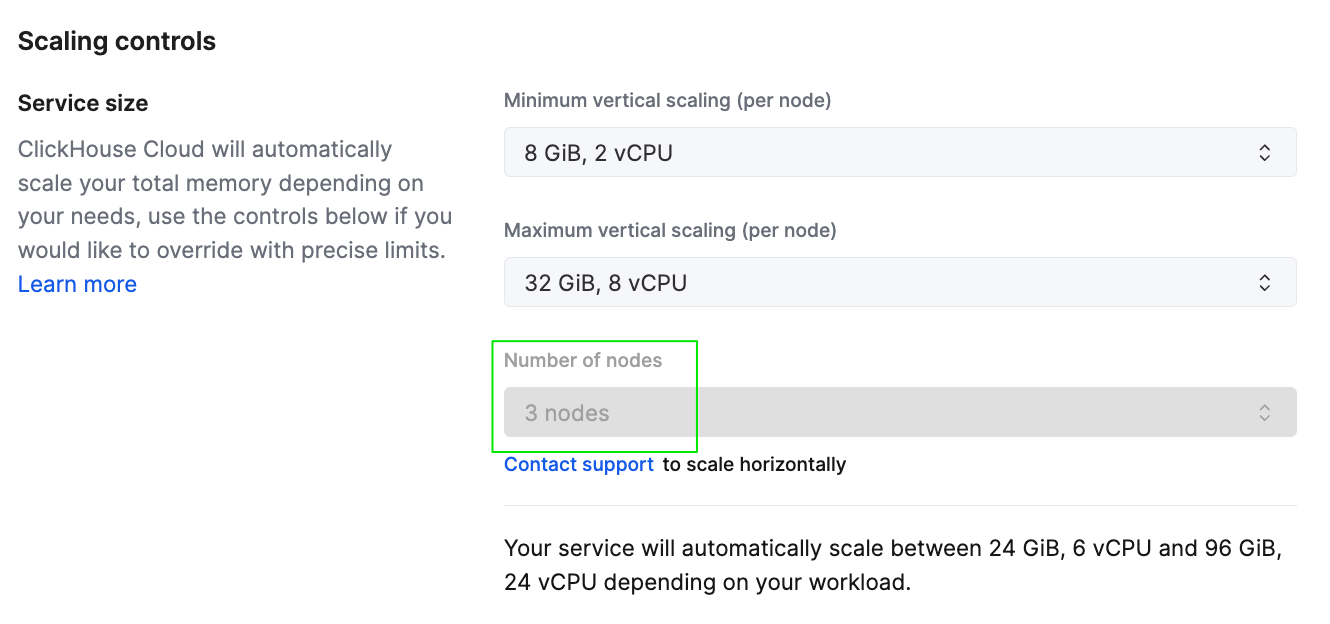
Service scaling settings from the ClickHouse Cloud console
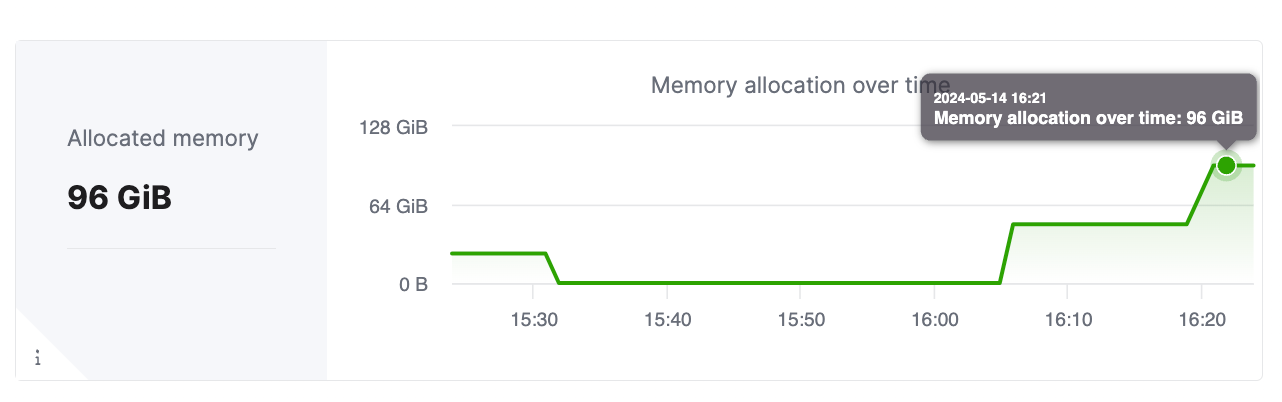
Once the service has scaled, the metrics dashboard in the cloud console should show the right allocation to the service. The screenshot below shows the cluster having scaled to total memory of 96 GiB, which is 6 replicas, each with GiB memory allocation.
Automatic Idling
In the Settings page, you can also choose whether or not to allow automatic idling of your service when it is inactive as shown in the image above (i.e. when the service is not executing any user-submitted queries). Automatic idling reduces the cost for your service as you are not billed for compute resources when the service is paused.
Use automatic idling only if your use case can handle a delay before responding to queries, because when a service is paused, connections to the service will time out. Automatic idling is ideal for services that are used infrequently and where a delay can be tolerated. It is not recommended for services that power customer-facing features that are used frequently.
Handling bursty workloads
If you have an upcoming expected spike in your workload, you can use the ClickHouse Cloud API to preemptively scale up your service to handle the spike and scale it down once the demand subsides. To understand the current service size and the number of replicas, you can run the query below:
SELECT *
FROM clusterAllReplicas('default', view(
SELECT
hostname() AS server,
getSetting('max_threads') as cpu_cores,
formatReadableSize(getSetting('max_memory_usage')) as memory
FROM system.one
))
ORDER BY server ASC
SETTINGS skip_unavailable_shards = 1